Extrapolation of high-order correlation energies: the WMS model†
Abstract
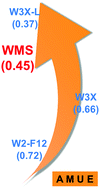
We have developed a new composite model chemistry method called WMS (Wuhan–Minnesota scaling method) with three characteristics: (1) a composite scheme to approximate the complete configuration interaction valence energy with the affordability condition of requiring no calculation more expensive than CCSD(T)/jul-cc-pV(T+d)Z, (2) low-cost methods for the inner-shell correlation contribution and scalar relativistic correction, and (3) accuracy comparable to methods with post-CCSD(T) components. The new method is shown to be accurate for the W4-17 database of 200 atomization energies with an average mean unsigned error (averaged with equal weight over strongly correlated and weakly correlated subsets of the data) of 0.45 kcal mol−1, and the performance/cost ratio of these results compares very favorably to previously available methods. We also assess the WMS method against the DBH24-W4 database of diverse barrier heights and the energetics of the reactions of three strongly correlated Criegee intermediates with water. These results demonstrate that higher-order correlation contributions necessary to obtain high accuracy for molecular thermochemistry may be successfully extrapolated from the lower-order components of CCSD(T) calculations, and chemical accuracy can now be obtained for larger and more complex molecules and reactions.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...
