Gas-phase ozonolysis of furans, methylfurans, and dimethylfurans in the atmosphere†
Abstract
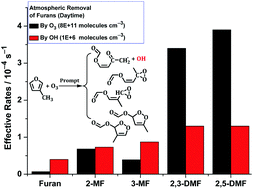
Furan and its methyl substituents, as promising alternative and renewable fuels and feedstock in the chemical industry, could be emitted to the atmosphere in a large scale and be degraded there by their reactions with OH, O3, NO3, Cl, etc. In this study, we investigate the mechanism of gas-phase ozonolysis of furans using quantum chemistry and kinetic calculations. The predicted rate coefficients agree well with the available experimental values for furan, 3-methylfuran (3-MF), and 2,5-dimethylfuran (2,5-DMF), suggesting that their removal by ozonolysis could be comparable to their removal by OH radicals in the atmosphere, particularly for methylfurans. Rate coefficients for the ozonolysis of furaldehydes were also calculated. The ozonolysis of furans follows the Criegee mechanism by forming primary ozonides (POZs). RRKM-ME calculations show that the decomposition of the POZs is dominated by the formation of β-unsaturated Criegee intermediates (CIs as ![[double bond splayed left]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e009.gif) C
C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) CR–CHOO or
CR–CHOO or ![[double bond splayed left]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e009.gif) C
C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) CR–C(OO)CH3, R = H or CH3). These CIs, formed with high excitation up to 250–280 kJ mol−1, would isomerize promptly to dioxirane and dioxolene products or dissociate promptly to a vinoxy-type radical and an OH radical. The dioxolenes would further isomerize to ether products containing another two carbonyl groups or one carbonyl group and one epoxide group, e.g., HC(O)OC(O)CH2CHO and HC(O)O–[CHOCH]–CHO in furan. Formation of OH radicals is expected for furans with alkyl substitution at 3-/4-positions such as 3-MF and 2,3-DMF. The predicted fractional yield of 0.31 for OH radicals in the ozonolysis of 3-MF agrees well with the previous experimental values of 0.59 (with an uncertainty factor of ca. 1.5).
CR–C(OO)CH3, R = H or CH3). These CIs, formed with high excitation up to 250–280 kJ mol−1, would isomerize promptly to dioxirane and dioxolene products or dissociate promptly to a vinoxy-type radical and an OH radical. The dioxolenes would further isomerize to ether products containing another two carbonyl groups or one carbonyl group and one epoxide group, e.g., HC(O)OC(O)CH2CHO and HC(O)O–[CHOCH]–CHO in furan. Formation of OH radicals is expected for furans with alkyl substitution at 3-/4-positions such as 3-MF and 2,3-DMF. The predicted fractional yield of 0.31 for OH radicals in the ozonolysis of 3-MF agrees well with the previous experimental values of 0.59 (with an uncertainty factor of ca. 1.5).


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...