Spatial distribution of organic functional groups supported on mesoporous silica nanoparticles (2): a study by 1H triple-quantum fast-MAS solid-state NMR†
Abstract
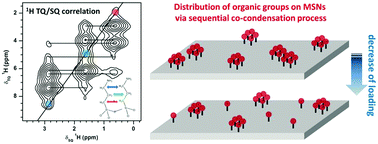
The distribution of organic functional groups attached to the surface of mesoporous silica nanoparticles (MSNs) via co-condensation was scrutinized using 1D and 2D 1H solid-state NMR, including the triple-quantum/single-quantum (TQ/SQ) homonuclear correlation technique. The excellent sensitivity of 1H NMR and high resolution provided by fast magic angle spinning (MAS) allowed us to study surfaces with very low concentrations of aminopropyl functional groups. The sequential process, in which the injection of tetraethyl orthosilicate (TEOS) into the aqueous mother liquor was followed by dropwise addition of the organosilane precursor, resulted in deployment of organic groups on the surface, which were highly clustered even in a sample with a very low loading of ∼0.1 mmol g−1. The underlying mechanism responsible for clustering could involve fast aggregation of the aminopropyltrimethoxysilane (APTMS) precursor within the liquid phase, and/or co-condensation of the silica-bound molecules. Understanding the deposition process and the resulting topology of surface functionalities with atomic-scale resolution, can help to develop novel approaches to the synthesis of complex inorganic–organic hybrid materials.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...
