Contagious degradation of a chemically active surface on the cathodes of lithium-ion batteries†
Abstract
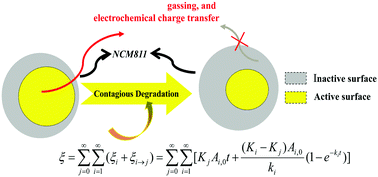
Durability is critically important in energy storage applications. Based on the model of the contagious degradation of a chemically active surface (CDCAS), a general model for durability has been systematically built. In practical lithium-ion batteries (LIBs), gassing swelling, limited by slow electrochemical processes, occurs over years of use and causes the LIB cell to rupture at an unpredictable moment. As an example of an application, the proposed CDCAS model was used to quantitatively study the gassing behaviors of different LIB systems, resulting in important information that can be used to predict swelling and avoid an accident. Interestingly, what could be deduced from the high nickel system (NCM811) model is that the active reaction area directly degrades to an inactive area without passing through an intermediate active area. The new degradation mechanism of the NCM811 cathode is further supported by the constant activation energy of the charge-transfer (Ea = 0.65 eV) across the whole high temperature storage test. This information shows that it was only partially correct, and even sometimes wrong, to use the increased thickness of the reconstructed rock-salt layer on the surface of some high-Ni cathode particles as an indicator of an increase in the impedance. The in-depth understanding on cathode degradation using the CDCAS model presented in this work will be beneficial for the development of high-safety and high-performance LIBs.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...