Carbon-contacted single molecule electrical junctions
Abstract
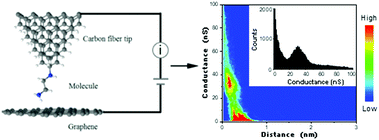
A fully metal-free molecular junction (MJ) has been built by using an electrochemically etched carbon fibre STM tip as the top electrode and graphene as the bottom electrode. The corresponding conductance values for 1,n-alkanediamine and 1,n-alkanedithiol (n = 2, 4, 6, 8 and 10) have been measured using the STM-I(s) technique. The tunnelling decay constant of the alkanediamine and alkanedithiol junctions with these carbon contacts is much lower than the corresponding metal contacted junctions of 0.24 and 0.38 per –CH2 unit, but the junction conductance with these carbon contacts is also lower. The carbon fibre tip can be considered a good candidate as an electrode. Compared with a gold tip, the carbon fibre tip leads to correspondingly lower molecular junction conductance.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...