Chemical and substitutional doping, and anti-site and vacancy formation in monolayer AlN and GaN†
Abstract
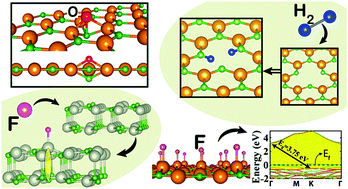
We investigated the effects of chemical/substitutional doping, hydrogenation, and anti-site and vacancy defects on the atomic, optoelectronic and magnetic properties of AlN and GaN monolayers. Upon doping of selected atoms, AlN and GaN monolayers can acquire magnetic properties, and their fundamental band gaps are modified by the localized gap states. Spin-polarized gap states broaden into bands at patterned coverage of adatoms, whereby half-metallic or magnetic semiconducting properties can be attained. Specific adatoms adsorbed to Ga atoms break the nearest vertical Ga–N bonds in the GaN bilayer in the heackelite structure and result in changes in the electronic and atomic structure. While adjacent and distant pairs of anion + cation vacancies induce spin polarization with filled and empty gap states, anti-site defects remain nonmagnetic; but both defects induce dramatic changes in the band gap. Fully hydrogenated monolayers are stable only for specific buckled geometries, where one geometry can also lead to an indirect to direct band gap transition. Also, optical activity shifts to the ultra-violet region upon hydrogenation of the monolayers. While H2 and O2 molecules are readily physisorbed on the surfaces of the monolayers with weak van der Waals attraction, they can be dissociated into constituent atoms at the vacancy site of the cation. Our study performed within density functional theory shows that the electronic, magnetic and optical properties of AlN and GaN monolayers can be tuned by doping and point defect formation in order to acquire diverse functionalities.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...