Prediction of the binding mode and resistance profile for a dual-target pyrrolyl diketo acid scaffold against HIV-1 integrase and reverse-transcriptase-associated ribonuclease H†
Abstract
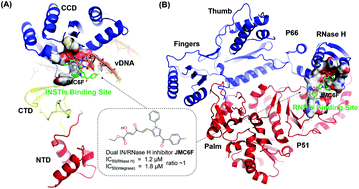
The rapid emergence of drug-resistant variants is one of the most common causes of highly active antiretroviral therapeutic (HAART) failure in patients infected with HIV-1. Compared with the existing HAART, the recently developed pyrrolyl diketo acid scaffold targeting both HIV-1 integrase (IN) and reverse transcriptase-associated ribonuclease H (RNase H) is an efficient approach to counteract the failure of anti-HIV treatment due to drug resistance. However, the binding mode and potential resistance profile of these inhibitors with important mechanistic principles remain poorly understood. To address this issue, an integrated computational method was employed to investigate the binding mode of inhibitor JMC6F with HIV-1 IN and RNase H. By using per-residue binding free energy decomposition analysis, the following residues: Asp64, Thr66, Leu68, Asp116, Tyr143, Gln148 and Glu152 in IN, Asp443, Glu478, Trp536, Lys541 and Asp549 in RNase H were identified as key residues for JMC6F binding. And then computational alanine scanning was carried to further verify the key residues. Moreover, the resistance profile of the currently known major mutations in HIV-1 IN and 2 mutations in RNase H against JMC6F was predicted by in silico mutagenesis studies. The results demonstrated that only three mutations in HIV-1 IN (Y143C, Q148R and N155H) and two mutations in HIV-1 RNase H (Y501R and Y501W) resulted in a reduction of JMC6F potency, thus indicating their potential role in providing resistance to JMC6F. These data provided important insights into the binding mode and resistance profile of the inhibitors with a pyrrolyl diketo acid scaffold in HIV-1 IN and RNase H, which would be helpful for the development of more effective dual HIV-1 IN and RNase H inhibitors.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...