Structural characterization of metal complexes in aqueous solutions: a XAS study of stannous fluoride†
Abstract
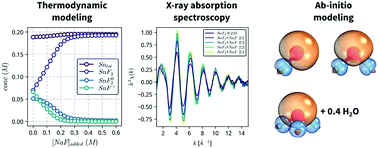
The identity and structure of tin(II)-fluoride complexes formed in aqueous solutions is determined by combining X-ray absorption spectroscopy, thermodynamic modeling and quantum mechanical calculations. Spectroscopic measurements confirm the presence of 3 stannous fluoride complexes, SnF+, SnF02 and SnF3−, with mean Sn–F bond distances that increase linearly, from 1.98 to about 2.04 Å, as a function of the coordination number. Computational ab initio calculations indicate that the stannous fluoride complexes form localized σs–p bonds, with the stereochemically active lone pair of the Sn(II) atom distorting the geometry of the complexes. In addition, the SnF3− complex exhibits loosely coordinated water, which is removed upon addition of glycerol to lower the solvent activity. Our results provide spectroscopic confirmation of the stannous fluoride complexes proposed in the literature, and explain why glycerol additions stabilize solutions of Sn(II) against oxidation.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...