Copolymers of poly(3-thiopheneacetic acid) with poly(3-hexylthiophene) as hole-transporting material for interfacially engineered perovskite solar cell by modulating band positions for higher efficiency†
Abstract
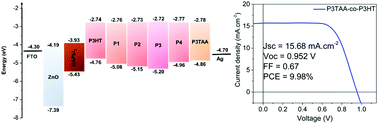
In order to tune the band positions of the hole-transporting material (HTM) in an interfacially engineered perovskite solar cell (PSC), random copolymers of poly(3-thiopheneacetic acid) and poly(3-hexylthiophene) (P3TAA-co-P3HT) with different compositions were produced by oxidative polymerization. The copolymers were characterized using 1H NMR, FTIR, and UV-vis spectroscopy and gel permeation chromatography. Here, ZnO nanoparticles were used as the electron-transporting material (ETM) and methylammonium lead iodide (MAPbI3) perovskite was used as the light-absorbing material to form an FTO/ZnO/MAPbI3/copolymer/Ag device, of which the power conversion efficiency (PCE) was found to be dependent on the copolymer composition and reached a maximum (∼10%) at a P3TAA content of 43 mol% in the copolymer (P3). The band gaps of the copolymers as determined from UV-vis spectroscopy and cyclic voltammetry exhibit a staggered-gap hetero-interface configuration in which the HOMO and LUMO of P3 closely match those of MAPbI3 and give rise to the maximum PCE. Time-resolved photoluminescence spectra of MAPbI3/HTM samples indicate that charge transfer across the perovskite/copolymer interface was faster with a reduced recombination rate for a P3 sample. The electrochemical impedance spectra (EIS) of the PSCs exhibit Nyquist plots with two semicircles, which correspond to an equivalent circuit consisting of two parallel R-C and R-CPE circuits connected in series. Analysis of the data indicates that the effective electron lifetime was longest for the P3 copolymer, which indicates that the charge recombination was lower than that in the components and other copolymers. The copolymers exhibited an intermediate stability with respect to their components, and amongst the copolymers P3 exhibited the highest stability.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...