Atomic-scale description of interfaces in rutile/sodium silicate glass–crystal composites
Abstract
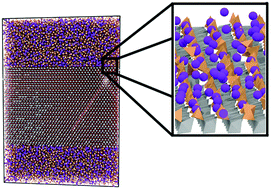
In this work interfaces between (Na2O)x(SiO2)1−x glasses (for x = 0.0, 0.1 and 0.2) and TiO2 crystals are simulated using molecular dynamics and empirical potentials. Interfaces are presented for the distinct terminating surfaces of TiO2 with Miller indices ≤2, the properties of which have been investigated using atomistic models. Simulations showed that partially ordered layers had been induced in the glass close to the interfaces, with successive oxygen-rich and cation-rich planes being noted. The first silicate layer in contact with the crystal tended to be highly-structured, with Si ions occupying well-defined positions that depend on the orientation of the crystal at the interface, and showing 2-dimensional ordering depending on glass composition. Finally, interface energies were calculated. These indicated that the interface formation may stabilise a crystal surface in comparison to maintaining a free surface. Results are presented suggesting that the structural flexibility of the glass network allows it to conform to the crystal, thereby providing charge compensation and avoiding large relaxation of the crystal structure close to the interfaces. Such interfacial properties could be crucial to improving phenomenological models of glass–crystal composite properties.
- This article is part of the themed collection: 2018 PCCP HOT Articles


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...