Long-distance perturbation on Schiff base–counterion interactions by His30 and the extracellular Na+-binding site in Krokinobacter rhodopsin 2†
Abstract
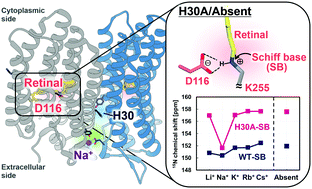
Krokinobacter rhodopsin 2 (KR2), a light-driven Na+ pump, is a dual-functional protein, pumping protons in the absence of Na+ when K+ or larger alkali metal ions are present. A specific mutation in helix A near the extracellular Na+ binding site, H30A, eliminates its proton pumping ability. We induced structural changes in H30A by altering the alkali metal ion bound at the extracellular binding site, and observed a strong electrostatic interaction between the Schiff base and counterion and torsion around the Schiff base as revealed by solid-state nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) and Fourier transform infrared (FTIR) spectroscopies. The strong interaction when His30 was absent and no ion bound at the extracellular binding site disabled retinal reisomerization, as was shown with flash-photolysis, forming a small amount of only a K-like intermediate. This revealed why H30A lacks the proton pumping function. Long-distance perturbation of the binding site and Schiff base revealed that a non-transported ion binding at the extracellular site is essential for pumping.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...