Hamiltonian replica exchange simulations of glucose oxidase adsorption on charged surfaces
Abstract
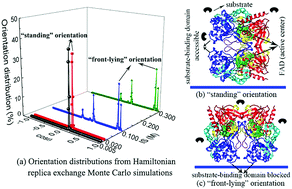
The Hamiltonian replica exchange Monte Carlo (H-REMC) algorithm was applied to study protein adsorption and its performance was compared with that of the temperature replica exchange Monte Carlo (T-REMC). Comparisons indicate that the simulation results are consistent but the computational efficiency is improved for H-REMC. H-REMC could accurately and efficiently identify the preferred orientations of glucose oxidase (GOx) on charged surfaces; different preferential GOx orientations on different surfaces and solution conditions could be spotted with a much fewer number of simulation runs. On positively charged surfaces, when electrostatic interactions dominate, the negatively charged GOx can be easily adsorbed with the “standing” orientation for which the substrate-binding domain is accessible to substrates. As the surface charge densities decrease and ionic strengths increase, there is an increasing contribution from the van der Waals (vdW) interactions, and thus more possible orientations appear. When the vdW interactions dominate, the unfavorable “front-lying” becomes the preferred orientation for which the substrate-binding domain is blocked by the surface. On negatively charged surfaces, though GOx has a net charge of −30 e under physiological conditions, the charged groups are unevenly distributed over the protein surface; the positive potential regions in the “back” of GOx enable the protein to be adsorbed on negatively charged surfaces with the “back-lying” orientation. The H-REMC provides an alternative method to accurately and efficiently probe the lowest-energy orientation of proteins adsorbed on surfaces for biotechnological applications.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...