Magnetization switching through domain wall motion in Pt/Co/Cr racetracks with the assistance of the accompanying Joule heating effect†
Abstract
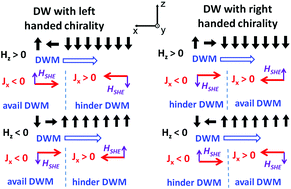
Heavy metal/ferromagnetic layers with perpendicular magnetic anisotropy (PMA) have potential applications for high-density information storage in racetrack memories and nonvolatile magnetic random access memories. In these devices, deterministic magnetization switching has been achieved via electric current induced spin orbital torques (SOTs) with the assistance of a current directional external in-plane bias field, which causes technological obstacles for the real application of SOT based spintronic devices. Here, we report that reversible field-free magnetization switching could be achieved via current-driven domain wall motion (DWM) in Pt/Co/Cr micro-sized racetracks with PMA owing to the preformation of the homochiral Néel-type domain wall, in which an in-plane inherent Dzyaloshinskii–Moriya interaction field was generated acting as the external in-plane bias field to break the symmetry. A full magnetization switching can be realized in this device based on the enhanced SOTs from a dedicated design of Pt/Co/Cr structures with Pt and Cr showing opposite signs of spin Hall angles. Therefore, the generated spin currents are expected to work in concert to improve the SOTs. We also demonstrated that the simultaneously accompanying Joule heating effect also plays a key role in the field-free magnetization switching process, including the propagation field as well as the domain wall motion velocity.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...