Influence of a silver salt on the nanostructure of a Au(111)/ionic liquid interface: an atomic force microscopy study and theoretical concepts†
Abstract
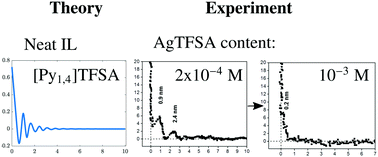
Ionic liquids (ILs) form a multilayered structure at the solid/electrolyte interface, and the addition of solutes can alter it. For this purpose, we have investigated the influence of the silver bis(trifluoromethylsulfonyl)amide (AgTFSA) concentration in 1-butyl-1-methylpyrrolidinium bis(trifluoromethylsulfonyl)amide ([Py1,4]TFSA) on the layering using in situ atomic force microscopy. AFM investigations revealed that the Au(111)/electrolyte interface indeed depends on the concentration of the salt where a typical “ IL” multilayered structure is retained only at quite low concentrations of the silver salt (e.g. ≤200 μM). However, at 200 μM AgTFSA/[Py1,4]TFSA and above this “IL” multilayered structure is disturbed/varied. A simple double layer structure was observed at 500 μM AgTFSA in [Py1,4]TFSA. Furthermore, the widths of the innermost layers have been found to be dependent on the concentration and on the applied electrode potentials. Our AFM results show that the concentration of solutes strongly influences the structure of the electrode/electrolyte interface and can provide new insights into the electrical double layer structure of the electrode/ionic liquid interface. We also introduce a semi-continuum theory to discuss the double layer structure.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...