Influence of aluminates on the structure and dynamics of water and ions in the nanometer channel of calcium silicate hydrate (C–S–H) gel
Abstract
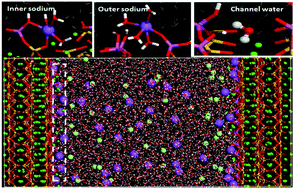
The transport and adsorption behavior of ions and water in nanometer pores is influenced by the composition of the substrate. In this paper, to understand the effect of Al species on the properties of confined nanofluids, molecular dynamics is utilized to study the structure, dynamics and interfacial adsorption behavior of NaCl solution confined in the gel pores of C–S–H and C–A–S–H. The bridging silicate tetrahedron substituted by the aluminate species enhances the hydrophilic properties of C–S–H gel. As compared with water on the C–S–H surface, the water layered packing is densified and the magnitude of dipole moment is enlarged for water located in the vicinity of the C–A–S–H surface. This is mainly attributed to the increasing number of H bonds contributed by oxygen atoms in the aluminate silicate chains sharing more negativity. Furthermore, C–A–S–H gel immobilizes more sodium and chloride ions on the surface than C–S–H. Sodium ions can coordinate with about two to three oxygen atoms in the aluminate tetrahedron tessellated in the narrow vacancy of the silicate channel, forming inner adsorbed species. Weak interactions between Cl and the substrate are due to the few ionic pairs between Cl ions and surface-accumulated Na ions. Due to the strong Na–Os binding on the C–A–S–H surface, the diffusion coefficient of the Na ions confined in the nanometer pores is reduced by 50% and the hydration time for the Na ions associated with surrounding water is increased by 40% as compared with bulk solution.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...