A density functional theory study of aldehydes and their atmospheric products participating in nucleation†
Abstract
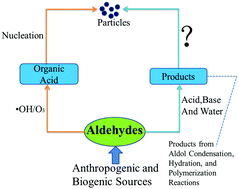
Aldehydes have been speculated as important precursor species in the formation of new atmospheric particles. In the present work, quantum chemical calculations were performed to investigate the hydrogen bonding interaction and the Gibbs free energy of formation (ΔG) for clusters consisting of sulfuric acid and aldehydes as well as their atmospheric reaction products. Calculations were conducted at 298 K and 1 atm at the M06-2X/6-311+G(3df,3pd) level. The results show that the addition of aldehyde compounds to H2SO4 unlikely contributes to new particle formation. However, their products from aldol condensation, hydration, and polymerization reactions can promote new particle formation by stabilizing sulfuric acid in the first step of nucleation. Moreover, the favorability of the interaction in the absence of water between sulfuric acid and the addition products is as follows: the hydration products > aldol condensation > aldehydes, but the results may be changed if water molecules are added. In particular, the calculated ΔG values imply that the monohydrate of glyoxal is more likely to nucleate with H2SO4 in comparison with ammonia in the presence or absence of water.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...