Enhanced room-temperature ferromagnetism on (In0.98−xCoxSn0.02)2O3 films: magnetic mechanism, optical and transport properties
Abstract
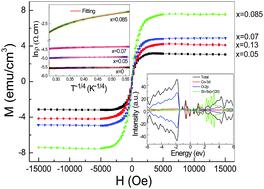
The effects of Co doping on the structural, optical, magnetic and transport properties of (In0.98−xCoxSn0.02)2O3 films grown by RF-magnetron sputtering were systematically investigated by theoretical and experimental techniques. The detailed structural analyses revealed that all the (In0.98−xCoxSn0.02)2O3 films possess the cubic bixbyite structure, with the substitutional Co at the In3+ sites of the In2O3 matrix, while some of the Co atoms form Co metal clusters. Obvious room-temperature (RT) ferromagnetic behavior was observed and the saturated magnetization (Ms) first increased, then decreased with increased Co concentration, while carrier concentration nc decreased monotonically, implying that the Co metal clusters are superparamagnetic and the observed RT ferromagnetism is not mediated by the charge carriers. The Mott variable range hopping (VRH) and hard band gap hopping transport behavior dominates the conduction mechanism of the films, confirming that the carriers are strongly localized. The UV-Vis and photoluminescence (PL) measurements indicate the decreased optical band gap Eg with Co doping, and further prove that the oxygen vacancies and Co impurity band form defect complexes of donor–acceptor pairs. The density functional theoretical calculations show that the codoped Sn can change the magnetic coupling between two Co ions from antiferromagnetic to ferromagnetic by the new hybridization between the Co 3d states with the Sn induced donor band. It can be concluded that the bound magnetic polaron (BMP) based oxygen vacancies as well as the Co–O–Co ferromagnetic superexchange interaction induced by Sn codoping may be responsible for the intrinsic ferromagnetic ordering in the (In0.98−xCoxSn0.02)2O3 films. These results may provide new insight for understanding the magnetic mechanism of In2O3 based DMS systems.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...