Acid–base machines: electrical work from neutralization reactions†
Abstract
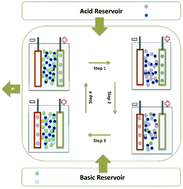
We have developed an electrochemical system that performs electrical work due to changes in alkaline ion and proton activities associated with acidic solution neutralization. This system can be used to treat wastewater, contributing to sustainable growth. The system includes an electrochemical machine that operates between an acidic and a basic reservoir to produce work in cycles comprising four stages: two isothermal ionic insertion/de-insertion steps and two steps involving acid and base injection. On the basis of the mixing free energy associated with the reaction free energy, we have developed the thermodynamic formalism by considering reversible electrochemical processes to determine the maximum work performed by this acid–base machine and the efficiency. Electrochemical methods in the time and frequency domains helped in investigating the kinetics of sodium ions and proton insertion in host matrices consisting of copper hexacyanoferrate and phosphomolybdic acid, respectively, to improve our understanding of the factors underlying dissipation as a function of pH and pNa. The full cell composed of these insertion electrodes was used as a proof of concept. It performed a maximum work of 26.4 kJ per mol of electro-inserted ion from HCl solution neutralization with the addition of NaOH, to simulate acidic wastewater treatment in a profitable and sustainable way.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...