Tuning the electronic environment of zinc ions with a ligand for dendrite-free zinc deposition in an ionic liquid†
Abstract
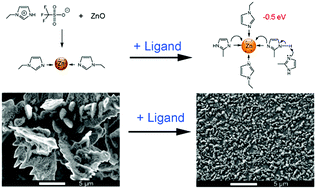
In this work, we report on the influence of an organic ligand on the electrodeposition of Zn from an ionic liquid (IL) electrolyte. Zinc oxide was first dissolved in a protic IL. By introducing a 2-methylimidazole (2-MIm) ligand, the electronic environment of zinc ions, Zn(II) complexes and the structure of the IL are considerably altered, as verified by both X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) and Raman spectroscopy. Due to the electron donation effect of the ligand, the zinc ions become less positively charged and exhibit a lower binding energy by −0.5 eV, compared to its absence. The atomic force microscopy (AFM) results show that a higher push-through force is required to rupture the interfacial layers in the presence of the ligand compared to its absence. The ligand can interact with both the cation and the anion of the IL via hydrogen bonds, forming compact layers on the surface, which also has a strong influence on the electrochemical performance. The cyclic voltammograms show reduction peaks at −1.4 V in all cases, but the current density decreases as the concentration of 2-MIm increases. Dendritic zinc deposits were obtained in 1.5 mol L−1 ZnO/[EIm]TfO, while dendrite-free zinc structures were obtained in the presence of 1.5 mol L−1 2-MIm.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...