In situ observation of Pt oxides on the low index planes of Pt using surface enhanced Raman spectroscopy†
Abstract
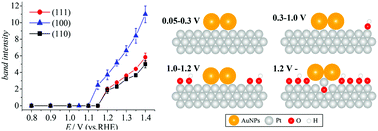
In situ vibrational spectra of Pt oxides that cannot be measured with IR spectroscopy have been studied on the low index planes of Pt using surface enhanced Raman spectroscopy with bare Au nanoparticles (NPSERS). Two bands appear around 570 and 340 cm−1 at higher potentials in 0.1 M HClO4 saturated with Ar, which are assigned to the stretching vibration of Pt–O(H) and the libration vibration of Pt–O, respectively. NPSERS spectra are measured in O2 saturated solution for the first time. The band intensities of Pt–O(H) and Pt–O in O2 saturated solution are enhanced significantly compared with those in Ar saturated solution. The onset potentials of Pt–O and Pt–O(H) formation are 1.15 V(RHE) on Pt(100) and 1.2 V(RHE) on Pt(111) and Pt(110). The onset potential of Pt–O and Pt–O(H) and band shape differ from the results obtained using shell isolated surface enhanced Raman spectroscopy (SHINERS). The Pt–O and Pt–O(H) band intensities are normalized using COad as an internal standard. The Pt–O(H) band intensity depends on surface structures as Pt(110) < Pt(111) ≪ Pt(100), whereas the Pt–O band gives a different intensity order for Pt(111) and Pt(110) as Pt(111) ≤ Pt(110) ≪ Pt(100) in O2 saturated solution.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...