Catalytic mechanism of phenylacetone monooxygenases for non-native linear substrates†
Abstract
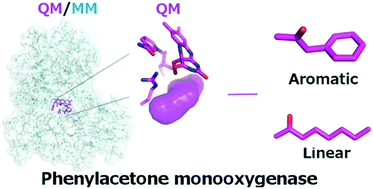
Phenylacetone monooxygenase (PAMO) is the most stable and thermo-tolerant member of the Baeyer–Villiger monooxygenase family, and therefore it is an ideal candidate for the synthesis of industrially relevant compounds. However, its limited substrate scope has largely limited its industrial applications. In the present work, we provide, for the first time, the catalytic mechanism of PAMO for the native substrate phenylacetone as well as for a linear non-native substrate 2-octanone, using molecular dynamics simulations, quantum mechanics and quantum mechanics/molecular mechanics calculations. We provide a theoretical basis for the preference of the enzyme for the native aromatic substrate over non-native linear substrates. Our study provides fundamental atomic-level insights that can be employed in the rational engineering of PAMO for wide applications in industrial biocatalysis, in particular, in the biotransformation of long-chain aliphatic oils into potential biodiesels.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...