Reaction mechanism and product branching ratios of the CH + C3H4 reactions: a theoretical study†
Abstract
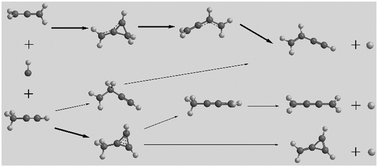
Two ground-state CH radical reactions with the C3H4 isomers allene and methylacetylene occurring along the C4H5 potential energy surface (PES) were studied to probe the reaction mechanisms and final product distributions. The calculations were performed using a CCSD(T)-F12//B2PLYPD3 PES in combination with the 1-D chemical master equation. The reaction between the CH radical and allene was found to lead to exclusive “funneling” of the energized C4H5 intermediates into linear C4H5 configurations before reaching the exit channels, regardless of the specific nature of the initial bimolecular reactive encounter. In the case of the CH radical reaction with methylacetylene, energized C4H5 three-membered ring structures underwent H loss in significant amounts resulting in the production of a cyclic C4H4 methylenecyclopropene product, in accordance with experiments. The theoretical product distribution at room temperature for methylacetylene + CH was ∼35% methylenecyclopropene, ∼36% vinylacetylene, and ∼28% 1,2,3-butatriene, which is in agreement with the available experimental data. The distribution for allene + CH was ∼93% vinylacetylene, ∼4% 1,2,3-butatriene and ∼3% acetylene + vinyl, which overestimates the experimental yield of vinylacetylene and underestimates that of 1,2,3-butatriene by ∼10%. The possible reasons for this slight quantitative deviation of the theoretical results obtained within statistical treatment from the experiment are discussed.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...