Structural evolution and dielectric properties of suspensions of carbon nanotubes in nematic liquid crystals†
Abstract
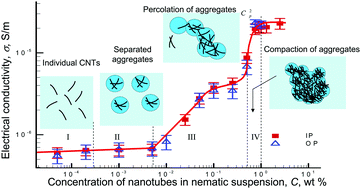
Structuring of carbon nanotubes (CNTs) in liquid crystals (LCs) and electro-physical characteristics of LC + CNT suspensions were studied in a very broad range of CNT concentrations, C, from 10−5 wt% (highly diluted suspensions) to 2.5 wt% (highly viscous suspensions). Along with the conventional sandwich cells with the transparent electrodes on the substrates, we used the cells with the in-plane applied electrical field in order to monitor changes of electrical parameters in the same direction as the structural changes observed under an optical microscope. The data revealed four stages of structural evolution with the increase of C: (1) dispersion of individual CNTs and their very small aggregates (C < 3 × 10−4 wt%), (2) presence of branched aggregates with a non-compact structure (C = 3 × 10−4–5 × 10−3 wt%), (3) percolation of non-compact aggregates (C = 5 × 10−3–10−1 wt%) and (4) compaction of aggregates and formation of a dense network (C = 10−1−1 wt%). In the studied concentration range, the conductivity displayed two percolation thresholds at C1p ≈ 0.004 wt% and C2p ≈ 0.5 wt%, which are associated with the formation of a non-compact and dense CNT network. By contrast, the permittivity ε′ revealed only one percolation threshold at C2p ≈ 0.5 wt%, when the distance between the adjacent CNTs becomes incredibly small.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...