Protic ammonium carboxylate ionic liquids: insight into structure, dynamics and thermophysical properties by alkyl group functionalization†
Abstract
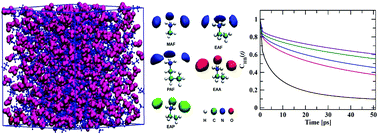
This study is aimed at characterising the structure, dynamics and thermophysical properties of five alkylammonium carboxylate ionic liquids (ILs) from classical molecular dynamics simulations. The structural features of these ILs were characterised by calculating the site–site radial distribution functions, g(r), spatial distribution functions and structure factors. The structural properties demonstrate that ILs show greater interaction between cations and anions when alkyl chain length increases on the cation or anion. In all ILs, spatial distribution functions show that the anion is close to the acidic hydrogen atoms of the ammonium cation. We determined the role of alkyl group functionalization of the charged entities, cations and anions, in the dynamical behavior and the transport coefficients of this family of ionic liquids. The dynamics of ILs are described by studying the mean square displacement (MSD) of the centres of mass of the ions, diffusion coefficients, ionic conductivities and hydrogen bonds as well as residence dynamics. The diffusion coefficients and ionic conductivity decrease with an increase in the size of the cation or anion. The effect of alkyl chain length on ionic conductivity calculated in this article is consistent with the findings of other experimental studies. Hydrogen bond lifetimes and residence times along with structure factors were also calculated, and are related to alkyl chain length.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...