Characterization of fine particles using optomagnetic measurements†
Abstract
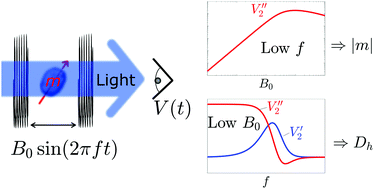
The remanent magnetic moment and the hydrodynamic size are important parameters for the synthesis and applications of magnetic nanoparticles (MNPs). We present the theoretical basis for the determination of the remanent magnetic moment and the hydrodynamic size of MNPs with a narrow size distribution using optomagnetic measurements. In these, the 2nd harmonic variation of the intensity of light transmitted through an MNP suspension is measured as a function of an applied axial oscillating magnetic field. We first show how the measurements of the optomagnetic signal magnitude at a low frequency vs. magnetic field amplitude can be used to determine the MNP moment. Subsequently, we use linear response theory to describe the dynamic non-equilibrium response of the MNP suspension at low magnetic field amplitudes and derive a link between optomagnetic measurements and magnetic AC susceptibility measurements. We demonstrate the presented methodology on two samples of commercially available multi-core MNPs. The results compare well with those obtained by dynamic light scattering, AC susceptibility and vibrating sample magnetometry measurements on the same samples when the different weighting of the particle size in the techniques is taken into account. The optomagnetic technique is simple, fast and does not require prior knowledge of the concentration of MNPs and it thus has the potential to be used as a routine tool for quality control of MNPs.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...