Theoretical characterization of the conformational features of unnatural oligonucleotides containing a six nucleotide genetic alphabet†
Abstract
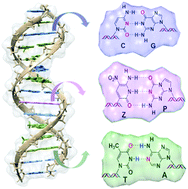
The addition of the unnatural P:Z base pair to the four naturally occurring DNA bases expands the genetic alphabet and yields an artificially expanded genetic information system (AEGIS). Herein, the structural feature of oligonucleotides containing a novel unnatural P:Z base pair is characterized using both molecular dynamics and quantum chemistry. The results show that the incorporation of the novel artificial base pair (P:Z) preserves the global conformational feature of duplex DNA except for some local structures. The Z-nitro group imparts new properties to the groove width, which widens the major groove. The unnatural oligonucleotides containing mismatched base pairs exhibit low stability. This ensures efficient and high-fidelity replication. In general, the incorporation of the P:Z pair strengthens the stability of the corresponding DNA duplex. The calculated results also show that the thermostability originates from both hydrogen interaction and stacking interaction. The Z-nitro group plays an important role in enhancing the stability of the H-bonds and stacking strength of the P:Z pair. Overall, the present results provide theoretical insights in the exploration of artificially expanded genetic information systems.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...