Efficient charge transfer and utilization of near-infrared solar spectrum by ytterbium and thulium codoped gadolinium molybdate (Gd2(MoO4)3:Yb/Tm) nanophosphor in hybrid solar cells
Abstract
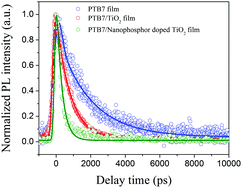
In this work, thulium and ytterbium codoped gadolinium molybdate (Gd2(MoO4)3:Yb/Tm) nanophosphors (NPs) have been synthesized, followed by being incorporated into a photo-catalytic titania (TiO2) nanoparticle layer. In detail, morphology and phase identification of the prepared NPs are first characterized and then the up-conversion of the Gd2(MoO4)3:Yb/Tm NPs is studied. Electron transfer dynamics after interfacing with bare or NP-doped electron donor TiO2 and the corresponding photovoltaic performance of solar cells are explored. The results show that Gd2(MoO4)3:Yb/Tm NPs excited at 976 nm exhibit intense blue (460–498 nm) and weak red (627–669 nm) emissions. The lifetime of electron transfer is shortened from 817 to 316 ps after incorporating NPs and correspondingly the electron transfer rate outstrips by 3 times that of the bare TiO2. Consequently, a notable power conversion efficiency of 4.15% is achieved as compared to 3.17% of pure TiO2/PTB7. This work demonstrates that the co-doping of robust rare earth ions with different unique functions can widen the harvesting range of the solar spectrum, boost electron transfer rate and eventually strengthen device performance, without complicated interfacial and structural engineering.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...