Micro-heterogeneity versus clustering in binary mixtures of ethanol with water or alkanes
Abstract
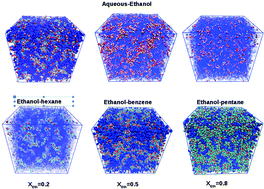
Ethanol is a hydrogen bonding liquid. When mixed in small concentrations with water or alkanes, it forms aggregate structures reminiscent of, respectively, the direct and inverse micellar aggregates found in emulsions, albeit at much smaller sizes. At higher concentrations, micro-heterogeneous mixing with segregated domains is found. We examine how different statistical methods, namely correlation function analysis, structure factor analysis and cluster distribution analysis, can describe efficiently these morphological changes in these mixtures. In particular, we explain how the neat alcohol pre-peak of the structure factor evolves into the domain pre-peak under mixing conditions, and how this evolution differs whether the co-solvent is water or alkane. This study clearly establishes the heuristic superiority of the correlation function/structure factor analysis to study the micro-heterogeneity, since cluster distribution analysis is insensitive to domain segregation. Correlation functions detect the domains, with a clear structure factor pre-peak signature, while the cluster techniques detect the cluster hierarchy within domains. The main conclusion is that, in micro-segregated mixtures, the domain structure is a more fundamental statistical entity than the underlying cluster structures. These findings could help better understand comparatively the radiation scattering experiments, which are sensitive to domains, versus the spectroscopy-NMR experiments, which are sensitive to clusters.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...