Thermoelectric properties of fullerene-based junctions: a first-principles study
Abstract
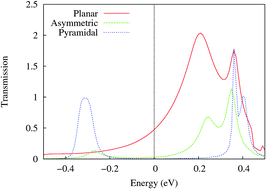
This study is built on density functional calculations in combination with the non-equilibrium Green's function, and we probe the thermoelectric transport mechanisms through C60 molecules anchored to Al nano-electrodes in three different ways, such as, the planar, pyramidal, and asymmetric surfaces. When the electrode is switched from the planar and pyramidal surfaces, the electrical conductance (σ) and electron's thermal conductance (κel) decrease almost two orders of magnitude due to the reduction of the molecule–electrode contact coupling, whereas the Seebeck coefficients (S) are reduced by ∼55%. Furthermore, the maximum electron's thermoelectric figure of merit (ZelT = S2σT/κel, assuming a vanishing phonon's thermal conductance) is about 0.12 in the asymmetric junction. In particular, all σ, S, κel, and ZelT increase along with the average temperature (T) in all C60-junctions, although their growth is really quite negligible in the pyramidal junction because the Fermi level is far away from the frontier orbitals. In addition, when the strain increases from the compressive (−1.0 Å) to tensile (1.0 Å) strain, the Seebeck coefficient in the planar junction increases drastically, while the Seebeck coefficients in the asymmetric and pyramidal junctions reach their maximum values at 0.2 Å tensile and −0.4 Å compressive strains, respectively. This is because the Seebeck coefficient is inversely proportional to the magnitudes and proportional to the slopes of the transmission spectrum around the Fermi level. Finally, it is found that the shift of the Fermi level is an effective scheme to obtain the maximum ZelT of any molecular junction, including fullerene-based junctions.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...