UV laser photoactivation of hexachloroplatinate bound to individual nucleobases in vacuo as molecular level probes of a model photopharmaceutical†
Abstract
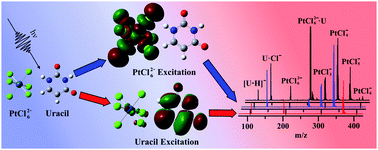
Isolated molecular clusters of adenine, cytosine, thymine and uracil bound to hexachloroplatinate, PtCl62−, have been studied using laser electronic photodissociation spectroscopy to investigate photoactivation of a platinum complex in the vicinity of a nucleobase. These metal complex–nucleobase clusters represent model systems for identifying the fundamental photochemical processes occurring in photodynamic platinum drug therapies that target DNA. This is the first study to explore the specific role of a strongly photoactive platinum compound in the aggregate complex. Each of the clusters studied displays a broadly similar absorption spectra, with a strong λmax ∼ 4.6 eV absorption band and a subsequent increase in the absorption intensity towards higher spectral-energy. The absorption bands are traced to ligand-to-metal-charge-transfer excitations on the PtCl62− moiety within the cluster, and result in Cl−·nucleobase and PtCl5− as primary photofragments. These results demonstrate how selective photoexcitation can drive distinctive photodecay channels for a model photo-pharmaceutical. In addition, cluster absorption due to excitation of nucleobase-centred chromophores is observed in the region around 5 eV. For the uracil cluster, photofragments consistent with ultrafast decay of the excited state and vibrational predissociation on the ground-state surface are observed. However, this decay channel becomes successively weaker on going from thymine to cytosine to adenine, due to differential coupling of the excited states to the electron detachment continuum. These effects demonstrate the distinctive photophysical characteristics of the different nucleobases, and are discussed in the context of the recently recorded photoelectron spectra of theses clusters.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...