Computational insights into CdSe quantum dots' interactions with acetate ligands†
Abstract
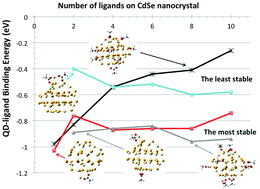
Using density functional theory (DFT) and time-dependent DFT (TDDFT), we investigate the effects of carboxylate groups on the electronic and optical properties of CdSe quantum dots (QDs). We specifically focus on the mechanisms of the binding of the acetate anion to the QD surface with and without excess of Cd2+ cations. Our calculations show that the most stable ligated conformations are those where an acetate is attached to extra Cd2+ ion forming a [Cd2+(CH3COO−)] at the QD's surface, while also accompanied by an acetate attached nearby at the surface balancing the overall neutral charge of the system. In contrast, formation of a neutral metal–acetate complex [Cd2+(CH3COO−)2] at the QD surface is found to be the least energetically preferable. A strength of the QD–ligand interaction depends on the solvent, the facet of the QD to which the ligands are attached, and the binding mode – with the bridging mode found to be the most stable conformation for both acetate and cadmium acetate ligands. The cadmium acetate ligands introduce electron trap states at the edge of the conduction band – unoccupied orbitals predominately localized on Cd2+ ion – that are extremely sensitive to the ligand position and the solvent polarity. Polar solvents like acetonitrile delocalize the electronic density over the entire system and, thus, eliminate trap states. As a result, mixed passivation of the CdSe QDs by pairs of cadmium acetate and acetate ligands provides optimal optical properties with minimal contributions of the ligand-related trap states and optically bright lowest energy transitions.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...