Cononsolvency behavior of hydrophobes in water + methanol mixtures
Abstract
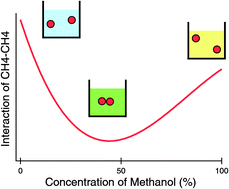
The molecular origin of cononsolvency behavior is explored using molecular dynamics simulations. Cononsolvency behavior in aggregations of methane molecules and conformational changes of those clusters dissolved in water + methanol mixtures are confirmed by re-entrant changes in the solvent-mediated interactions with increasing methanol concentration. The results indicate that the cononsolvency behavior arises from the solute–solute hydrophobic interactions rather than other interactions such as solute–solvent hydrophilic interactions. Furthermore, we show that even the van der Waals interaction is not necessary to induce the cononsolvency behavior by investigating the dimerization process of repulsive cavities. The non-monotonic change of the solvent-mediated interaction results from the difference in the concentration dependencies of excess chemical potentials between an isolated methane and methane clusters. The concentration dependencies of the excess chemical potentials are decomposed into contributions from various intermolecular effective interactions through the framework of the Kirkwood–Buff theory, and then we show that the change of the relative magnitude between hydrophobe–methanol and hydrophobe–water effective interactions with increasing methanol concentration is responsible for the cononsolvency behavior.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...