The photocatalytic properties of ultrathin bismuth oxychloride nanosheets: a first principles study†
Abstract
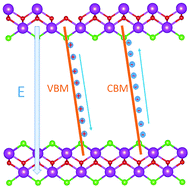
Two-dimensional (2D) nanosheet structures have obvious advantages with respect to their bulk counterparts in photocatalytic reaction due to their extraordinary electronic and optical properties. So do the 2D BiOCl nanosheets with significant improvement of photocatalytic activity in the degradation of dyes shown by recent studies. In the present work, the surface energies, electronic structure and photocatalytic properties of ultrathin BiOCl nanosheets are examined by means of density functional theory to investigate the origin of their high photocatalytic performance. The results show that the Cl atom terminated BiOCl(001) surface possesses lower surface energy than others and is very likely to be introduced in the ultrathin nanosheet. Moreover, our proposed model accounts well for the origin of band edge upshift of the ultrathin BiOCl nanosheets with respect to BiOCl nanoplates observed in experiments. In addition, the presence of Bi vacancies on the surfaces of nanosheets can enhance the built-in electric field and further promote the separation of photo-generated carriers, which is extremely advantageous for the photocatalytic process. Our results provide a new insight into the high photocatalytic performance of BiOCl(001) nanosheets.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...