Formation of C3H2, C5H2, C7H2, and C9H2 from reactions of CH, C3H, C5H, and C7H radicals with C2H2†
Abstract
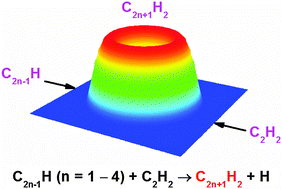
The Cm+2H2 family can be classified into two categories – C2n+1H2 and C2n+2H2. Cm+2H2 are important intermediates in the syntheses of large carbonaceous molecules. An understanding of the formation mechanisms of both odd and even carbon-numbered Cm+2H2 is beneficial to atmospheric, astronomical, and combustion chemistry. HC2n+2H (polyynes) are believed to be producible from C2nH + C2H2 and C2H + C2nH2 reactions but C2n+1H2 (n ≥ 2) attract less attention to their formation mechanisms. In the present study, we make up for the lack of knowledge on C2n+1H2 formation mechanisms by investigating the reactions C2n−1H + C2H2 → C2n+1H2 + H with n = 1–4. The dynamics of reactions of C2n−1H radicals with C2H2 are explored in crossed molecular beams using products C2n+1H2. The translational-energies and angular distributions of the hydrogen-loss channels of products are unraveled by measuring time-of-flight spectra and photoionization-efficiency spectra of C2n+1H2 with tunable synchrotron vacuum-ultraviolet ionization. The C2n+1H2 product includes two isomers, c-1HC2n−1(C)CH and 3HC2n+1H, which are identified by the maximal translational-energy release and the photoionization threshold. Furthermore, quantum-chemical calculations indicate that the title reactions incur a small or negligible entrance barrier and are nearly isoergic except for the barrierless exothermic reaction CH + C2H2 → C3H2 + H. We demonstrate for the first time that C5H2, C7H2, and C9H2 are producible from the title reactions. In conjunction with studies on the C2nH + C2H2 reactions, a brief picture for the CmH (m = 1–8) + C2H2 → Cm+2H2 + H reactions can be outlined.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...