Interplay between the hydrophobic effect and dipole interactions in peptide aggregation at interfaces†
Abstract
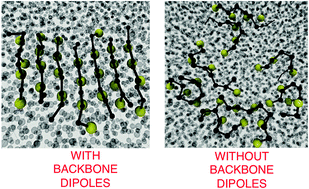
Protein misfolding is an intrinsic property of polypeptides, and misfolded conformations have a propensity to aggregate. In the past decade, the development of various coarse-grained models for proteins has provided key insights into the driving forces in folding and aggregation. We recently developed a low resolution Water Explicit Polarizable PROtein coarse-grained Model (WEPPROM) by adding oppositely charged dummy particles inside protein backbone beads. With this model, we were able to achieve significant α/β secondary structure content, without any added bias. We now extend the model to study peptide aggregation at hydrophobic–hydrophilic interfaces and draw comparisons to aggregation in explicit water solvent. Elastin-like octapeptides (GV)4 are used as a model system for this study. A condensation-ordering mechanism of aggregation is observed in water. Our results suggest that backbone interpeptide dipolar interactions, not hydrophobicity, plays a more significant role in fibril-like peptide aggregation. We observe a cooperative effect in hydrogen bonding or dipolar interactions, with an increase in aggregate size in water and at interfaces. Based on this cooperative effect, we provide a potential explanation for the observed nucleus size in peptide aggregation pathways. The presence of a hydrophobic–hydrophilic interface increases both (a) order of aggregates formed, and (b) rate of the aggregation process. Without dipolar particles, peptide aggregation is not observed at the hydrophilic–hydrophobic interface. Thus, the presence of dipoles, not hydrophobicity, plays a key role in aggregation observed at hydrophobic interfaces.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...