Copper(ii) complexes with peptides based on the second cell binding site of fibronectin: metal coordination and ligand exchange kinetics†
Abstract
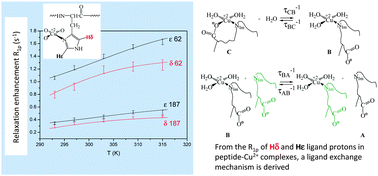
Copper(II) complexes with short peptides based on the second cell binding site of fibronectin, PHSFN and PHSEN, have been characterized by potentiometric, UV-vis, CD, EPR and NMR spectroscopic methods. The histidine imidazole nitrogen is the anchoring site for the metal ion binding. Thermodynamic and spectroscopic evidence is given that the side chain oxygen donor atom of glutamyl residue in Ac-PHSEN-NH2 is also involved in the binding up to physiological pH. To determine ligand exchange kinetic parameters after the imidazole nitrogen anchoring, proton relaxation enhancement NMR data have been collected for the two hydrogen atoms of the imidazole ring in the temperature range 293–315 K at pH 5.2 and globally treated within different kinetic models for ligand exchange. The best fitting model involves two steps. In the first one, which is slow, a water molecule disengages a carbonyl or a carboxylate group coordinated to the metal ion in the complex formed by PHSFN or PHSEN, respectively. This stage is one order of magnitude slower for PHSEN, due to entropic effects. In the second step, which is fast, the complex just formed exchanges with the ligand. In this step, no appreciable differences are found for the two cases examined.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...