Phase separation and crystallization in sodium lanthanum phosphate glasses induced by electrochemical substitution of sodium ions with protons
Abstract
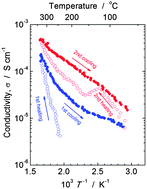
Electrochemical substitution of sodium ions with protons (alkali-proton substitution; APS), and the injection of proton carriers was applied to sodium lanthanum phosphate glasses. A clear and homogeneous material was obtained for a glass of composition 25NaO1/2–8LaO3/2–66PO5/2–1GeO2 following APS, with a resulting proton conductivity of 4 × 10−6 S cm−1 at 250 °C. The glass underwent phase separation and crystallization at temperatures >255 °C, forming a highly hygroscopic and proton conducting H3PO4 phase in addition to LaP5O14 and other unidentified phases. A glass of composition 25NaO1/2–8LaO3/2–67PO5/2 underwent phase separation and crystallization during APS, forming both H3PO4 and LaP5O14 phases. Sodium lanthanum phosphate glasses are prone to phase separation and crystallization during APS unlike the previously reported NaO1/2–WO3–NbO5/2–LaO3/2–PO5/2 glasses. The phase separation was explained by a reduction in viscosity following APS and the introduction of protons, which exhibit high field strength. Thus, phase separation and crystallization of glasses during APS was difficult to avoid. An approach to suppress phase separation is discussed.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...