Characterization of thin films of the solid electrolyte LixMg1−2xAl2+xO4 (x = 0, 0.05, 0.15, 0.25)†
Abstract
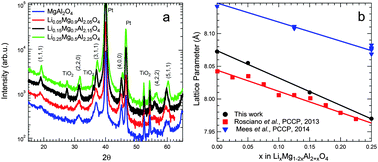
RF-sputtered thin films of spinel LixMg1−2xAl2+xO4 were investigated for use as solid electrolyte. The usage of this material can enable the fabrication of a lattice matched battery stack, which is predicted to lead to superior battery performance. Spinel LixMg1−2xAl2+xO4 thin films, with stoichiometry (x) ranging between 0 and 0.25, were formed after a crystallization anneal as shown by X-ray diffraction and transmission electron microscopy. The stoichiometry of the films was evaluated by elastic recoil detection and Rutherford backscattering and found to be slightly aluminum rich. The excellent electronic insulation properties were confirmed by both current–voltage measurements as well as by copper plating tests. The electrochemical stability window of the material was probed using cyclic voltammetry. Lithium plating and stripping was observed together with the formation of a Li–Pt alloy, indicating that Li-ions passed through the film. This observation contradicted with impedance measurements at open circuit potential, which showed no apparent Li-ion conductivity of the film. Impedance spectroscopy as a function of potential showed the occurrence of Li-ion intercalation into the LixMg1−2xAl2+xO4 layers. When incorporating Li-ions in the material the ionic conductivity can be increased by 3 orders of magnitude. Therefore it is anticipated that the response of LixMg1−2xAl2+xO4 is more adequate for a buffer layer than as the solid electrolyte.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...