Molecular basis of substrate translocation through the outer membrane channel OprD of Pseudomonas aeruginosa†
Abstract
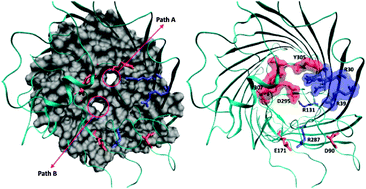
The objective of this study is to identify the structural features governing the transport of molecules through nanometric channel proteins at a molecular level. Our focus is to come up with a precise understanding of the structure and dynamics of the outer membrane porin OprD of the Gram-negative bacterium Pseudomonas aeruginosa by studying the translocation of natural amino acid residues/substrates through it. We used in silico electrophysiology and metadynamics simulation techniques as they can provide precise information on the molecule/channel interactions at the atomic scale that allows testing quantitative structure–function relationships. We performed our simulations on the whole OprD protein, with all loops modelled and without any constraints to keep the channel open. Dynamics of both internal and external loops and the polar nature of the eyelet region play important roles in modulating the translocation of molecules through OprD by creating two alternative paths for translocation. All positive residues take the main path upon binding in the negative pocket just above the constriction region. The same factor is unfavourable for negative substrates and hence they have a relatively high barrier for translocation. Differently, neutral substrates do not show any specificity and they can follow the two alternative paths.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...