Drawing dependent structures, mechanical properties and cyclization behaviors of polyacrylonitrile and polyacrylonitrile/carbon nanotube composite fibers prepared by plasticized spinning
Abstract
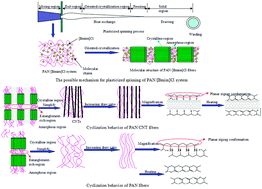
Drawing to change the structural properties and cyclization behaviors of the polyacrylonitrile (PAN) chains in crystalline and amorphous regions is carried out on PAN and PAN/carbon nanotube (CNT) composite fibers. Various characterization methods including Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy, differential scanning calorimetry, X-ray diffraction and thermal gravimetric analysis are used to monitor the structural evolution and cyclization behaviors of the fibers. With an increase of the draw ratio during the plasticized spinning process, the structural parameters of the fibers, i.e. crystallinity and planar zigzag conformation, are decreased at first, and then increased, which are associated with the heat exchange rate and the oriented-crystallization rate. A possible mechanism for plasticized spinning is proposed to explain the changing trends of crystallinity and planar zigzag conformation. PAN and PAN/CNT fibers exhibit various cyclization behaviors induced by drawing, e.g., the initiation temperature for the cyclization (Ti) of PAN fibers is increased with increasing draw ratio, while Ti of PAN/CNT fibers is decreased. Drawing also facilitates cyclization and lowers the percentage of β-amino nitrile for PAN/CNT fibers during the stabilization.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...