Interaction of iron with a wagon wheel-like ultrathin TiOx film grown on Pt(111)
Abstract
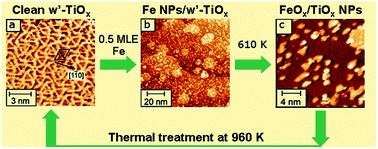
The structure and thermal evolution of Fe nanoparticles deposited on a wetting TiOx ultrathin film epitaxially grown on Pt(111) has been characterized by various surface science techniques. Combining the results obtained it is shown that, at room temperature, metallic Fe nucleates randomly and oxidizes at the interface. A thermal treatment causes Fe migration through the TiOx layer, forming a mixed oxide and a new hexagonal ultrathin film phase. Finally, the pristine TiOx phase motif is restored, due to the complete diffusion of Fe into the Pt substrate.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...