Highly efficient photocatalytic degradation of organic dyes by Cu doped ZnO nanostructures
Abstract
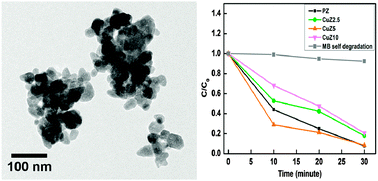
Copper doped ZnO nanostructures have been synthesized by a facile wet chemical method. Structural properties of as-synthesized nanomaterials have been studied by X-ray diffraction (XRD), field emission scanning electron microscopy (FESEM) and transmission electron microscopy (TEM) with energy dispersive X-ray spectroscopy, while UV-visible absorption spectroscopy and Raman spectroscopy have been used to study their optical properties. Sunlight driven photocatalytic degradation of methylene blue (MB) and methyl orange (MO) dyes in water was used to evaluate the photocatalytic activities of Cu doped ZnO nanostructures using UV-visible absorption spectroscopy. The results showed that there is an optimum Cu doping level which leads to the highly enhanced photocatalytic activity of Cu doped ZnO nanostructures, as compared to pure ZnO nanostructures. A mechanism for the enhanced photocatalytic activity of Cu–ZnO nanostructures is tentatively proposed. The enhanced photocatalytic activity of Cu–ZnO nanostructures is attributed to the combined effects of improved separation of photogenerated charge carriers due to optimal Cu doping in ZnO nanostructures and the formation of ZnO–CuO nanoheterojunctions.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...