Self-assembly of photoswitchable diblock copolymers: salt-induced micellization and the influence of UV irradiation†
Abstract
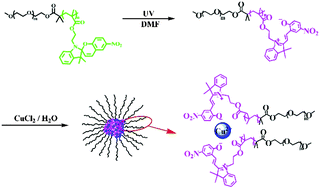
Salt-induced self-assemblies of poly(ethylene glycol-block-spiropyran methacrylate) (PEG-b-PSPMA) block copolymers were studied in this research. PEG-b-PSPMA block copolymers were dissolved in a 10 : 1 N,N-dimethyl-formamide (DMF)/water mixture. Upon ultraviolet light (UV) irradiation, the pendant spiropyran (SP) groups in the PSPMA blocks were isomerized into open merocyanine (MC) forms and the addition of inorganic salts (CuCl2, FeCl3 and Zn(CH3COO)2) induced micellization of PEG-b-PSPMA block copolymers in the solutions. In a salt-induced micelle, complexes formed by PSPMA and inorganic ions are in the cores and PEG chains are in the coronae. The reverse conversion of the isomers from MC form to SP form in the dark was studied by UV-vis, and the self-assembled aggregates were analyzed by dynamic light scattering (DLS) and transmission electron microscopy (TEM). The self-assembly of PEG-b-PSPMA in aqueous medium was also investigated. In aqueous solution, amphiphilic PEG-b-PSPMA self-assembled into micelles with the hydrophobic PSPMA blocks in the cores and the hydrophilic PEG blocks in the coronae. Upon UV irradiation, the hydrophobic SP units in the cores were isomerized into hydrophilic MC forms. The MC isomers have the attractive MC–MC interactions, and the reversion from MC to SP in the dark is difficult. DLS and TEM results both demonstrated that the micelles self-assembled by PEG-b-PSPMA did not disassemble upon UV irradiation, due to the attractive MC–MC interactions in the cores.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...