Quantum coherence effects in natural light-induced processes: cis–trans photoisomerization of model retinal under incoherent excitation
Abstract
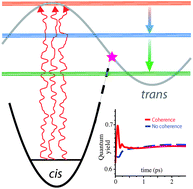
We present a theoretical study of quantum coherence effects in the primary cis–trans photoisomerization of retinal in rhodopsin induced by incoherent solar light. Using the partial secular Bloch–Redfield quantum master equation approach based on a two-state two-mode linear vibronic coupling model of the retinal chromophore [S. Hahn and G. Stock, J. Phys. Chem. B, 2000, 104, 1146–1149], we show that a sudden turn-on of incoherent pumping can generate substantial Fano coherences among the excited states of retinal. These coherences are the most pronounced in the regime where the matrix elements of the transition dipole moment between the ground and excited eigenstates are parallel to one another. We show that even when the transition dipole moments are perpendicular (implying the absence of light-induced Fano coherence) a small amount of excited-state coherence is still generated due to the coupling to intramolecular vibrational modes and the protein environment, causing depopulation of the excited eigenstates. The overall effect of the coherences on the steady-state population and on the photoproduct quantum yield is shown to be small; however we observe a significant transient effect on the formation of the trans photoproduct, enhancing the photoreaction quantum yield by ∼11% at 200 fs. These calculations suggest that coupling to intramolecular vibrational modes and the protein environment play an important role in photoreaction dynamics, suppressing oscillations in the quantum yield associated with Fano interference.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Measurement and prediction of quantum coherence effects in biological processes

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...