Preparation of Ni@C–Cd0.8Zn0.2S nanocomposites with highly efficient and stable photocatalytic hydrogen production activity
Abstract
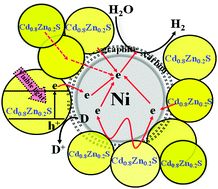
A series of carbon-coated Ni (Ni@C)–Cd0.8Zn0.2S nanocomposites were fabricated via a facile hydrothermal process using pre-prepared Ni@C as a starting material. The obtained products were characterized by X-ray diffraction, UV-Vis diffuse reflectance absorption spectroscopy, X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy and electron microscopy. It was found that the introduction of Ni@C nanoparticles can improve both the visible light-induced photocatalytic H2 production activity and stability of the Cd0.8Zn0.2S solid solution, and the Ni nanoparticles encapsulated by several graphite-like carbon layers show high chemical and thermal stability. Among those products with various Ni@C contents, the 5 wt% Ni@C–Cd0.8Zn0.2S nanocomposite exhibits the maximum photoactivity (969.5 μmol h−1) for H2 production, which is ∼3.10 times higher than that (312.6 μmol h−1) of pristine Cd0.8Zn0.2S. This significant enhancement in the photoactivity by loading Ni@C nanoparticles can be attributed to the metallic Ni in the Ni@C acting as a co-catalyst, while the graphite-like carbon shells acting as the Cd0.8Zn0.2S nanoparticles' support and electron acceptor, which causes an effective photogenerated carrier separation in space and an improvement in the photoactivity and stability for H2 production. The present findings demonstrate a cost reduction strategy by using a non-noble metal co-catalyst for efficient and stable light-to-hydrogen energy conversion.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...