Influence of surface functionalization on the hydrophilic character of mesoporous silica nanoparticles†
Abstract
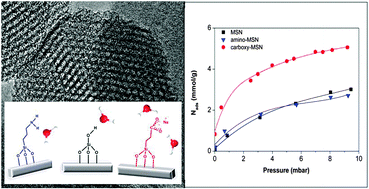
We report the synthesis and surface functionalization of MCM-41-like mesoporous silica nanoparticles (MSNs) with spheroidal shape and particle size of 141 ± 41 nm. The success of surface functionalization with aminopropyl and sodium ethylcarboxylate groups (giving amino-MSN and carboxy-MSN, respectively) was ascertained by infrared spectroscopy and ζ potential measurements. The former showed the decrease of surface silanol groups and the corresponding appearance of signals related to NH2 bending mode (δNH2) at 1595 cm−1 and COO− stretching (νas and νsym) at 1562 and 1418 cm−1. The latter showed a change in surface charge, in that the isoelectric point (IEP) changed from pH 3–4.5 to 8.5 when the MSN was functionalized with the amino groups, while carboxy-MSN showed a more negative charge in the whole pH range with respect to MSN. The hydrophilic character of the prepared materials was ascertained by quantitative microgravimetric measurements, allowing the calculation of the average isosteric adsorption heat (![[q with combining macron]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/i_char_0071_0304.gif) st). This was found to be 51 ± 3 kJ mol−1, 61 ± 4, and 65 ± 3 kJ mol−1 for MSN, amino-MSN, and carboxy-MSN samples, respectively. The increase in
st). This was found to be 51 ± 3 kJ mol−1, 61 ± 4, and 65 ± 3 kJ mol−1 for MSN, amino-MSN, and carboxy-MSN samples, respectively. The increase in ![[q with combining macron]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/i_char_0071_0304.gif) st after functionalization can be ascribed to the specific interaction of water molecules with the functionalizing agents, in agreement with a higher basicity with respect to silanol groups. Moreover, the possibility of multiple H-bonding interactions of water molecules with the carboxylate anion is put forward to account for the higher water uptake with respect to parent MSN.
st after functionalization can be ascribed to the specific interaction of water molecules with the functionalizing agents, in agreement with a higher basicity with respect to silanol groups. Moreover, the possibility of multiple H-bonding interactions of water molecules with the carboxylate anion is put forward to account for the higher water uptake with respect to parent MSN.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...