Boron nitride nanosheets as improved and reusable substrates for gold nanoparticles enabled surface enhanced Raman spectroscopy†
Abstract
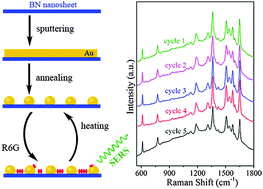
Atomically thin boron nitride (BN) nanosheets have been found to be excellent substrates for noble metal particles enabled surface enhanced Raman spectroscopy (SERS), thanks to their good adsorption of aromatic molecules, high thermal stability and weak Raman scattering. Faceted gold (Au) nanoparticles have been synthesized on BN nanosheets using a simple but controllable and reproducible sputtering and annealing method. The size and density of the Au particles can be controlled by sputtering time, current and annealing temperature etc. Under the same sputtering and annealing conditions, the Au particles on BN of different thicknesses show various sizes because the surface diffusion coefficients of Au depend on the thickness of BN. Intriguingly, decorated with similar morphology and distribution of Au particles, BN nanosheets exhibit better Raman enhancements than silicon substrates as well as bulk BN crystals. Additionally, BN nanosheets show no noticeable SERS signal and hence cause no interference to the Raman signal of the analyte. The Au/BN substrates can be reused by heating in air to remove the adsorbed analyte without loss of SERS enhancement.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...