Ionic liquid-induced all-α to α + β conformational transition in cytochrome c with improved peroxidase activity in aqueous medium†
Abstract
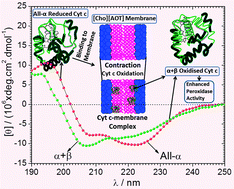
Choline dioctylsulfosuccinate [Cho][AOT] (a surface active ionic liquid) has been found to induce all-α to α + β conformational transition in the secondary structure of enzyme cytochrome c (Cyt c) with an enhanced peroxidase activity in its aqueous vesicular phase at pH 7.0. [Cho][AOT] interacted with Cyt c distinctly at three critical concentrations (aggregation C1, saturation C2 and vesicular C3) as detected from isothermal titration calorimetric analysis. Oxidation of heme iron was observed from the disappearance of the Q band in the UV-vis spectra of Cyt c upon [Cho][AOT] binding above C3. Circular dichroism analysis (CD) has shown the loss in both the secondary (190–240 nm) and tertiary (250–300 nm) structure of Cyt c in the monomeric regime until C1, followed by their stabilization until the pre-vesicular regime (C1 → C3). Loss in both the secondary and tertiary structure has been observed in the post-vesicular regime with the change in Cyt c conformation from all-α to α + β which is similar to the conformational changes of Cyt c upon binding with mitochondrial membrane (Biochemistry 1998, 37, 6402–6409), thus citing the potential utility of [Cho][AOT] membranes as an artificial analog for in vitro bio-mimicking. Fluorescence correlation spectroscopy (FCS) measurements confirm the unfolding of Cyt c in the vesicular phase. Dynamic light scattering experiments have shown the contraction of [Cho][AOT] vesicles upon Cyt c binding driven by electrostatic interactions observed by charge neutralization from zeta potential measurements. [Cho][AOT] has been found to enhance the peroxidase activity of Cyt c with maximum activity at C3, observed using 2,2′-azino-bis(3-ethylbenzothiazoline-6-sulfonic acid) diammonium salt as the substrate in the presence of hydrogen peroxide. This result shows the relevance of tuning ionic liquids to surfactants for bio-mimicking of specific membrane protein–lipid interactions.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...