Site reactivity in the free radicals induced damage to leucine residues: a theoretical study†
Abstract
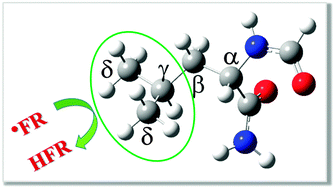
Several recent computational studies have tried to explain the observed selectivity in radical damage to proteins. In this work we use Density Functional Theory and Transition State Theory including tunnelling corrections, reaction path degeneracy, the effect of diffusion, and the role of free radicals to get further insights into this important topic. The reaction between a leucine derivative and free radicals of biological significance, in aqueous and lipid media, has been investigated. Both thermochemical and kinetic analyses, in both hydrophilic and hydrophobic environments, have been carried out. DPPH, ˙OOH, ˙OOCH3, ˙OOCH2Cl, ˙OOCHCl2 and ˙OOCHCH2 radicals do not react with the target molecule. The reactions are proposed to be kinetically controlled. The leucine gamma site was the most reactive for the reactions with ˙N3, ˙OOCCl3, ˙OCH3, ˙OCH2Cl, and ˙OCHCl2 radicals, with rate constants equal to 1.97 × 105, 3.24 × 104, 6.68 × 105, 5.98 × 106 and 8.87 × 108 M−1 s−1, respectively, in aqueous solution. The ˙Cl, ˙OH and ˙OCCl3 radicals react with leucine at the beta, gamma, and delta positions at rates close to the diffusion limit with the alpha position which is the slowest path and the most thermodynamically favored. The presented results confirm that the Bell–Evans–Polanyi principle does not apply for the reactions between amino acid residues and free radicals. Regarding the influence of the environment on the reactivity of the studied series of free radicals towards leucine residues, it is concluded that hydrophilic media slightly lower the reactivity of the studied radicals, compared to hydrophobic ones, albeit the trends in reactivity are very similar.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...