Site preference of NH3-adsorption on Co, Pt and CoPt surfaces: the role of charge transfer, magnetism and strain
Abstract
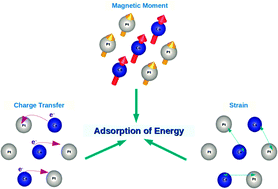
Oxidation of Co at the surface poses a major problem in the cyclable use of CoPt, a cost-effective catalyst for proton exchange membrane fuel cells. This can be alleviated by attaching a ligand selectively to Co-sites to stop its oxidation without compromising the catalytic activity. Here, we present a comparative analysis of adsorption of NH3 on the (0001) surface of Co in the HCP structure and (111) surfaces of Pt and CoPt alloy in the FCC structure, using first-principles density functional theoretical calculations. While NH3 binds more strongly with the Pt surface than with the Co surface, we find that its binding with the Co atom is stronger than that with the Pt atom on the surface of the CoPt alloy. Our analysis of the charge density and electronic structure shows how this originates from (a) the electron transfer from the minority spin d-band of Co to Pt, and (b) shift in the energy of d-bands and the magnetic moments of Co atoms on the surface of the CoPt alloy relative to those on the (0001) surface of Co. Hybridization of the d-states of Co in CoPt with pz states of N in NH3 used to stop Co oxidation also results in improving the charge transfer from Co to Pt that is relevant to the catalytic activity of CoPt. We finally present the analysis of how the interaction of NH3 with the CoPt surface can be tuned with strain.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...